Inclusion, Accessibility, Assisted digital needs - what’s the difference?
A short post to help define these terms
Accessibility
Usually, when they hear “Accessibility” most people think: screen readers, wheelchairs, and more recently they might even think of dyslexia for example. But there is much more to it:
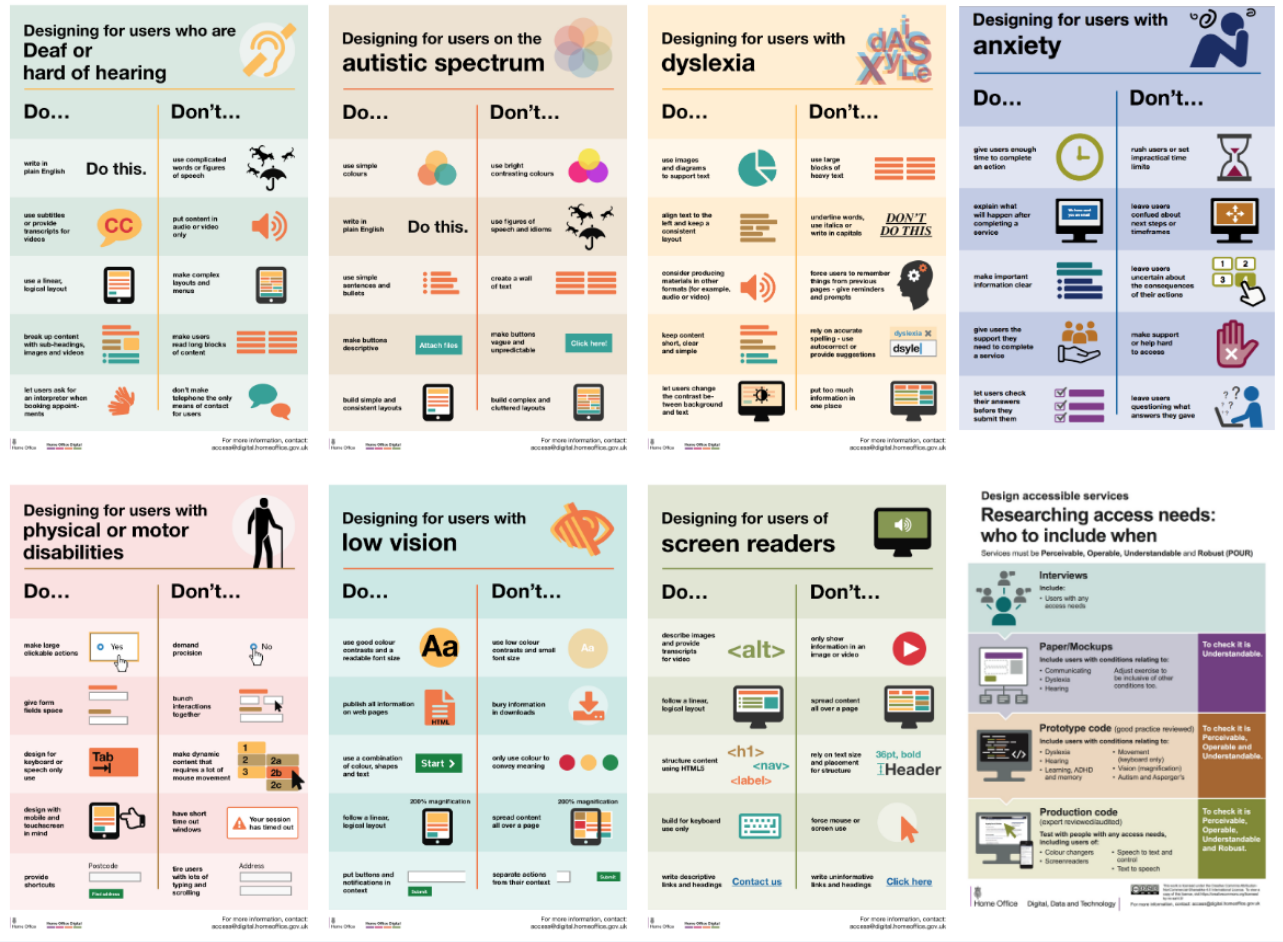
Do and Don’t posters from the Home Office
In the UK, 1 in 5 people have a disability
The concept of accessibility doesn’t just apply to people with disabilities — all users will have different needs at different times and in different circumstances.
The World Health Organization defines disability as:
“a mismatch in interaction between the features of a person’s body and the features of the environment in which they live.”
The impairment can be permanent, temporary or situational, but in the end, it’s the same requirements:
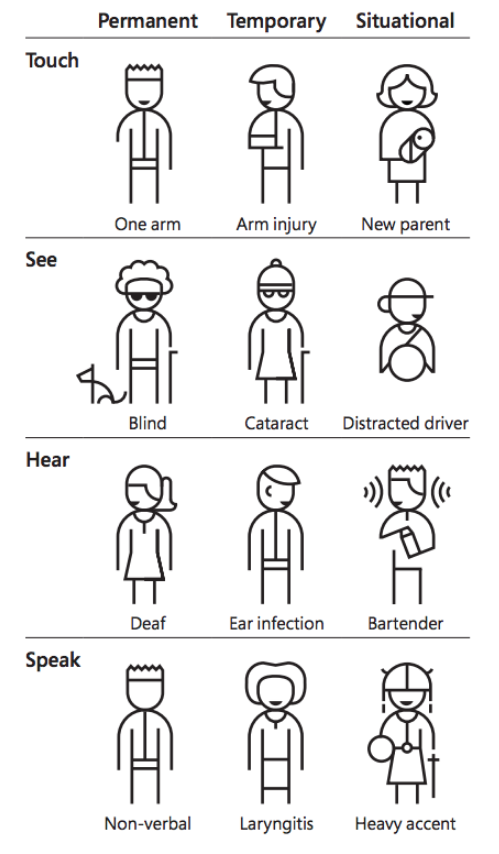
From the Inclusive toolkit Microsoft Design
Assisted Digital - Digital exclusion
Sometimes people need help to use services online. This is known as assisted digital support.
Any user may need assisted digital support, if they lack:
- trust in your service or the internet
- confidence to use an online service themselves
- access to the internet
- digital skills
- motivation to overcome these barriers on their own
A recent study shows that almost one-fifth of Britons ‘do not use internet’.
In this article, from the BBC, you get a better idea of the various reasons why people don’t use internet:
10% do not use the net because of privacy worries 40% of those earning less than £12,500 do not go online 70% of all respondents “uncomfortable” with targeted advertising and data tracking 12% have been hit by computer viruses 11% got abusive emails
Just like for accessibility, users will have different needs at different times and in different circumstances
For example:
- you might be comfortable doing online shopping but struggle for a specific task like uploading a document or taking a photo with your phone
- you’re visiting an area where there is nearly no signal or simply travelling on a train
- you have hardly any data left on your account, no or slow internet access
- you are applying online to get some support because you have been assaulted, or just lost someone, or about to lose your home
In Scotland - Digital exclusion
About 1 in 7 people in Scotland can’t get online. This is about 800,000 people.
There are various reasons:
- money: can’t afford a device, to pay for broadband/data, or to get the assistive devices they need
- lives in an area with poor infrastructure
- lack confidence to use an online service themselves
- lack digital skills
We usually don’t realise how many are affected:
- 2 in 10 adults in Scotland lack basic digital skills
- 1 in 10 have no digital skills (find info, order shopping online or fill in a form)
- 13% of households have no internet access at home (17% for the lowest income households)
- 1 in 8 adults do not use the internet at all
Sources: Scottish household survey 2018: annual report and UK Consumer Digital Index 2019 from the Lloyds Bank
- The economic impact of Digital Inclusion in the UK
- Measure to assess users’ digital competency
- Location, Privilege and Performant Websites
Inclusion
This is a broader term: Inclusive design is about designing for a diverse range of people. Whatever their gender, sexuality, age, ethnicity, social class, communications abilities or culture.
- if your service is not accessible, then you are not inclusive of people with accessibility needs
- if your service online is accessible, but you don’t offer an alternative for assisted digital users, then you are not inclusive either
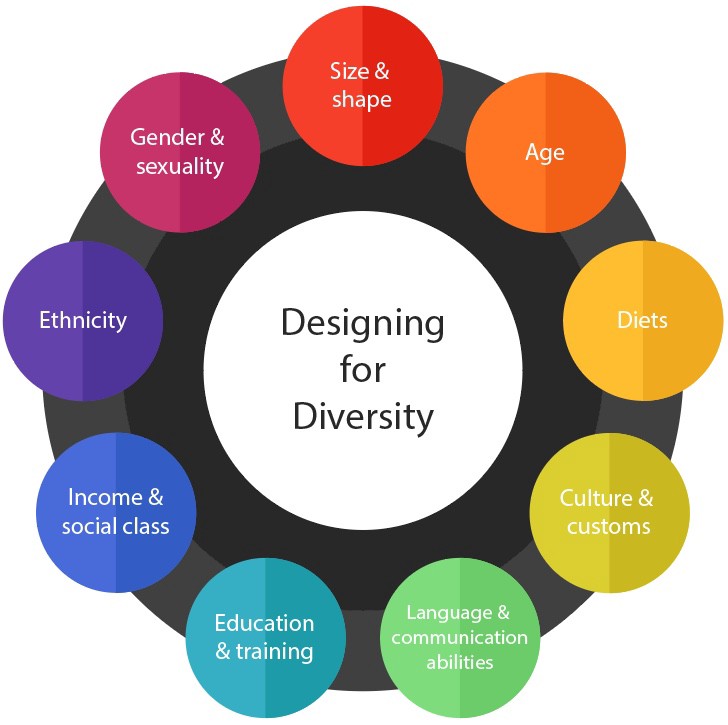
Common inclusion issues in services
For example asking for:
- your gender when it might not even be needed or in a way that doesn’t allow you to identify yourself correctly
- your title or marital status
- parents information in terms which exclude same-sex-parenting
Bakken & Bæck, a digital studio based in Oslo, Bonn and Amsterdam, have a very good Diversity and Inclusion guide if you want to learn more.
You can also check their A to Z Inclusion and diversity glossary.
This post was written to become part of the resources we will share on the Global Accessibility Awareness Day on Thursday 21 May 2020.
Written on 18 May 2020 by Stéphanie